Protect Your Digital Life: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing App Permissions on iPhone & Android
In our increasingly connected world, smartphones are extensions of ourselves, holding a treasure trove of personal data. From your photos and contacts to your location and health information, apps constantly seek access to various parts of your device. But do you truly understand what you’re agreeing to when you tap “Allow”? This article will demystify app permissions, explain their crucial importance, and provide clear, actionable steps for managing them on both iPhone and Android, empowering you to take control of your digital privacy.
What Exactly Are App Permissions?
App permissions are essentially requests from applications to access specific features or data on your smartphone. Think of them as digital keys that an app needs to unlock certain functionalities. For instance, a camera app needs permission to access your phone’s camera to take pictures. A messaging app might request access to your contacts to help you find friends already using the app.
These permissions are designed as a privacy safeguard, giving you a say in what information apps can see and what actions they can perform. Without your explicit consent, apps shouldn’t be able to freely browse your photo gallery, record your conversations, or track your every move.
Why Are App Permissions So Important?

The importance of managing app permissions cannot be overstated. Here’s why:
- Protecting Your Privacy: Many apps collect a vast amount of data, some of which is highly sensitive. Unchecked permissions can expose your health data, financial details, precise location, and even your habits to third parties. This data can be used for targeted advertising, sold to data brokers, or, in worst-case scenarios, exploited in security breaches.
- Preventing Misuse and Abuse: While most legitimate apps have valid reasons for requesting certain permissions, some might ask for more access than they truly need. This excessive access (often referred to as a “violation of Least Privilege”) can be exploited by malicious apps or lead to unintended data sharing.
- Saving Battery Life and Data: Permissions like “Location Services” or “Background App Refresh” can significantly drain your battery and consume mobile data if apps are constantly using them in the background. Limiting these can improve your phone’s performance.
- Enhancing Security: By understanding and controlling app permissions, you reduce your device’s attack surface. If an app doesn’t have access to your contacts, for example, a data breach involving that app can’t compromise your contact list.
Managing App Permissions: Your Step-by-Step Guide
Both iPhone and Android offer robust ways to manage app permissions, though the exact steps and terminology may vary slightly by OS version and device model.
On iPhone (iOS)
Apple’s approach to permissions is generally centralized and emphasizes user privacy from the get-go.
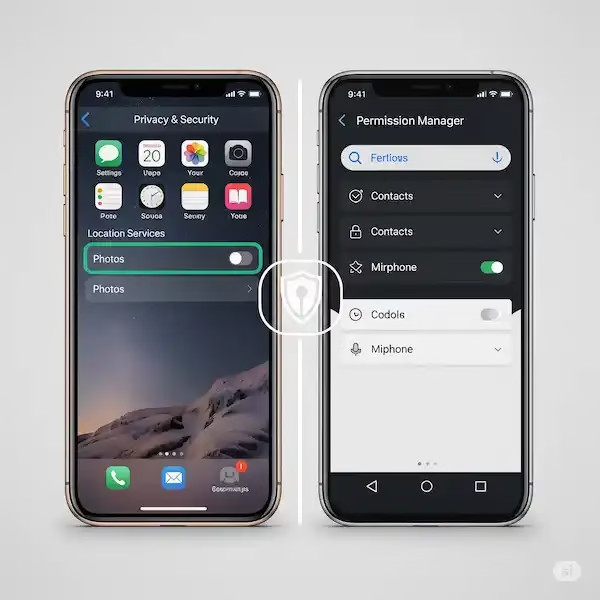
- Access Privacy & Security Settings:
- Open the Settings app.
- Scroll down and tap on Privacy & Security.
- Manage by Data Category:
- Within “Privacy & Security,” you’ll find a comprehensive list of data categories, such as:
- Location Services: Control which apps can access your precise or approximate location. You can often choose “While Using the App,” “Ask Next Time Or When I Share,” or “Never.”
- Contacts: See which apps have access to your address book.
- Photos & Videos: Manage access to your photo library (you can often choose “Add Photos Only,” “Limited Photos,” or “Full Access”).
- Microphone & Camera: Essential for communication and media apps.
- Health, Calendars, Reminders, Bluetooth, Local Network, Tracking, and more.
- Tap on any category to see a list of apps that have requested access to that specific data type.
- Toggle the switch next to each app to Allow or Deny access.
- Within “Privacy & Security,” you’ll find a comprehensive list of data categories, such as:
- Manage by Individual App:
- Go back to the main Settings app.
- Scroll down the list until you see all your installed apps.
- Tap on a specific app (e.g., “Facebook,” “WhatsApp”).
- Here, you’ll see all the permissions that app has requested. You can individually toggle each permission on or off. This section also allows you to manage notifications, cellular data usage, and background app refresh for that specific app.
- App Privacy Report:
- For an advanced overview, navigate to Settings > Privacy & Security > App Privacy Report.
- This feature provides a detailed timeline of when apps accessed your sensitive data (like camera, microphone, location, and photos) and their network activity. It’s an excellent tool for spotting unusual behavior.
On Android
Android’s permission management is also highly customizable, allowing you to fine-tune access for each app.
- Access App Permissions Manager:
- Open the Settings app.
- Tap on Apps (or “Apps & Notifications,” “Applications,” depending on your device).
- Tap Permission manager (or “Permissions”). This is a central hub that lists all permission types.
- Manage by Permission Type:
- Within the “Permission manager,” you’ll see categories like:
- Location: Control location access (often with options like “Allow all the time,” “Allow only while using the app,” “Ask every time,” or “Don’t allow”).
- Camera
- Microphone
- Contacts
- Files and media (formerly “Storage”)
- Calendar
- SMS
- And many more.
- Tap on a specific permission type to see which apps have been granted that permission.
- Tap on an app from the list, then choose your desired permission status (e.g., “Allow,” “Don’t allow”).
- Within the “Permission manager,” you’ll see categories like:
- Manage by Individual App:
- Go back to Settings > Apps.
- Tap See all apps (if not already listed).
- Select the specific app you want to manage.
- Tap Permissions.
- You’ll see a list of permissions granted and denied for that app. Tap on any permission to change its status.
- Special Access Permissions:
- Some Android devices also have a “Special app access” or “Advanced” section within the “Apps” settings. This area covers more powerful permissions like:
- Display over other apps (allows apps to draw on top of other apps)
- Install unknown apps
- Modify system settings
- Usage access (allows apps to see what other apps you’re using)
- Exercise extreme caution when granting these permissions.
- Some Android devices also have a “Special app access” or “Advanced” section within the “Apps” settings. This area covers more powerful permissions like:
Important Tips for Managing App Permissions
- Adopt the “Least Privilege” Principle: Only grant apps the absolute minimum permissions they need to function. If a flashlight app asks for access to your contacts, that’s a red flag!
- Review Before Installation (Android): Before installing an app from the Google Play Store, check its “Data safety” section (or “App permissions” on older versions). This provides an overview of the data the app collects and the permissions it requests.
- Pay Attention to Prompts: When an app first requests a permission, read the prompt carefully. Understand why the app needs that access.
- Regularly Review Permissions: Periodically go through your app permissions on both devices. As apps update, they might request new permissions. Remove permissions from apps you no longer use or those that have become overly intrusive.
- Utilize “While Using the App” or “Ask Every Time”: For sensitive permissions like location or microphone, choose options that limit access to when the app is actively in use, or prompt you each time. Avoid “Always Allow” unless absolutely necessary (e.g., for certain navigation apps).
- Consider Revoking Unused App Permissions (Android): Many newer Android versions offer a feature to automatically revoke permissions for apps you haven’t used in a while. Enable this in your app settings for added privacy.
- Be Wary of “All-or-Nothing” Permissions: If an app demands a broad range of unrelated permissions just to work, it might be worth finding an alternative.
- Delete Unused Apps: The simplest way to manage permissions is to uninstall apps you no longer use. If an app isn’t on your phone, it can’t access your data!
By actively managing your app permissions, you become the gatekeeper of your personal data. This proactive approach not only enhances your privacy and security but also contributes to a smoother, more efficient smartphone experience. Take a few moments today to review your settings – your digital well-being will thank you for it!
Understanding Third-Party App Permission Managers
Third-party app permission managers are applications developed by companies other than Apple or Google, designed to help users control and monitor what their installed apps can do. While the native permission systems are robust, these external tools often offer:
- More Granular Control: Beyond simple “allow” or “deny,” some managers can mock or “fake” data, providing an app with dummy information (e.g., a blank contact list) instead of blocking access entirely, which can prevent app crashes.
- Detailed Logging and Monitoring: Many provide logs of when apps accessed specific permissions, offering a clearer picture of an app’s behavior over time.
- Privacy Insights: They might offer insights into which apps are accessing your data most frequently or which permissions are most commonly requested across your app ecosystem.
- Automation: Some advanced tools allow for automated permission management based on user-defined rules.
It’s crucial to note that the availability and functionality of these apps differ significantly between iOS and Android due to the varying levels of system access Apple and Google allow third-party developers.
On iPhone (iOS)
Due to Apple’s stringent security architecture and sandboxing of apps, third-party permission managers on iOS have very limited direct control over system-level app permissions. Apple deliberately restricts third-party apps from deeply interacting with the core operating system to maintain user privacy and security.
Instead, iOS-based “permission managers” often focus on:
- Social Media and Connected Account Scanners: Apps like “MyPermissions Privacy Cleaner” (though its availability and active development may vary) primarily scan your connected accounts (Facebook, Google, etc.) to show you which third-party applications or services have been granted access to your data through those platforms. They help you revoke permissions from services connected via OAuth (Open Authorization).
- Privacy Reports and Insights: They might aggregate information that’s already available in Apple’s “App Privacy Report” in a different format or offer suggestions based on general privacy best practices.
- VPNs and Ad Blockers: Many privacy-focused apps on iOS are VPN services or content blockers that protect your network traffic and block trackers, rather than directly managing individual app permissions on your device.
Key takeaway for iOS: Do not expect a third-party app to grant you “root-level” control over app permissions similar to what might be available on a jailbroken iPhone or a rooted Android device. Apple’s native “Privacy & Security” settings and “App Privacy Report” remain the primary and most effective tools for managing app permissions on an un-modified iPhone.
On Android
Android’s open nature historically allowed for more powerful third-party app permission managers, especially on rooted devices. However, even on non-rooted devices, some tools leverage Android’s “App Ops” (Application Operations) functionality, which is a hidden permission control system within Android.
Types of third-party permission managers on Android include:
- App Ops Front-Ends: These apps provide a more user-friendly interface to Android’s built-in, but often hidden, App Ops functionality. They allow users to toggle individual operations (like “read clipboard” or “access boot completed”) that might not be directly exposed in the standard Android permission manager.
- Privacy Guards (Rooted Devices): For rooted Android devices, tools like XPrivacyLua (which requires the Xposed Framework) offer the most comprehensive and granular control. They can intercept and deny app requests for sensitive data, mock data, or even prevent apps from knowing that a permission was denied.
- Security Suites/Antivirus Apps: Many comprehensive security apps for Android include a permission management component that helps users review and understand app permissions, often flagging potentially risky apps.
- Application Analyzers: These apps scan your installed applications and report on the permissions they request, their potential privacy implications, and sometimes even their network activity.
Key takeaway for Android: While rooting offers the most advanced control, some non-root solutions exist that leverage App Ops, providing more granular control than the default Android settings. Always download these apps from trusted sources like the Google Play Store or F-Droid (for open-source apps) to avoid malware.
Comparison Chart of Features
Here’s a generalized comparison chart, acknowledging that specific features can vary greatly between individual third-party apps and their compatibility with different OS versions and device rooting status.
| Feature / Category | Native iOS Permission Manager | Native Android Permission Manager | Third-Party iOS Privacy Tool (e.g., MyPermissions) | Third-Party Android Permission Manager (e.g., App Ops front-end, XPrivacyLua) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Allow/Deny | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No (Indirectly via connected accounts) | ✅ Yes |
| Permission Categorization | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Per-App Permission Review | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Detailed Access Logs | ✅ Yes (App Privacy Report) | ❌ No (Basic history only) | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (Often more detailed than native) |
| “Mock” or Fake Data | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (Primarily on rooted devices) |
| Granular Sub-Permissions | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (Via App Ops or root tools) |
| Automated Rules/Profiles | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Some (More common on rooted devices) |
| Connected Account Scanning | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No (Not their primary focus) |
| Risk Assessment/Flags | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Some | ✅ Some (Often integrated into security suites) |
| Requires Root/Jailbreak | ❌ No | ❌ No (For basic features) | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (For advanced features like mocking) |
| System-wide Blocking | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (For certain permissions, especially rooted) |
| Ease of Use | High | Medium-High | Medium | Varies (Can be complex for advanced tools) |
Disclaimer: The landscape of third-party apps is constantly evolving. Apps may become unavailable, gain new features, or cease development. Always research the latest reviews and compatibility before installing any third-party tool.
Choosing the Right Tool for You to Manage App Permissions
For iPhone Users: Given Apple’s robust built-in privacy controls, a third-party app permission manager is generally not necessary for core system permissions. Focus on:
- Regularly reviewing your Settings > Privacy & Security options.
- Utilizing the App Privacy Report to monitor app behavior.
- Carefully managing permissions granted to apps via “Sign in with Apple” or other connected services.
- Considering a reputable VPN for network-level privacy.
For Android Users: If the native Android permission manager doesn’t offer enough control, and you’re comfortable with slightly more advanced usage:
- Non-rooted: Look for well-reviewed “App Ops” front-end apps from trusted developers on the Google Play Store or F-Droid. These can provide a more detailed look at permissions than the standard settings.
- Rooted: If you are willing to root your device, tools like XPrivacyLua offer unparalleled control, but come with inherent risks (voiding warranty, potential security vulnerabilities if not managed correctly).
Ultimately, the best “permission manager” is an informed and vigilant user. Whether you rely on native features or augment them with third-party tools, understanding what your apps can access is the first and most critical step in safeguarding your digital privacy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – Managing App Permissions
Q1: Do I need to manage app permissions manually, or can my phone do it automatically? A1: While your iPhone and Android devices have some automatic features (like revoking permissions for unused apps on newer Android versions), manual management is crucial. Regularly reviewing and adjusting permissions ensures you have full control over your data and that apps aren’t accessing more than they truly need.
Q2: What happens if I deny a permission that an app needs? A2: If you deny a crucial permission, the app might not function correctly, or at all. For example, a camera app won’t be able to take pictures if you deny camera access. Most apps will prompt you again to grant the necessary permission if it’s essential for a core function.
Q3: Can an app access my data if I haven’t granted it permission? A3: Generally, no. Modern operating systems like iOS and Android are designed to prevent apps from accessing sensitive data or features without your explicit permission. However, it’s always wise to only download apps from official and trusted app stores to minimize risks from malicious apps that might try to bypass these protections.
Q4: Is it safe to grant permissions like “Full Access” to my Photos? A4: Granting “Full Access” to your photos means the app can view, edit, and delete any photo in your library. While necessary for some editing apps, it’s safer to use “Limited Photos” (on iOS) or allow access only to specific media if the option is available. Always consider if the app truly needs full access.
Q5: What’s the difference between “Allow only while using the app” and “Always allow” for location? A5:
- “Allow only while using the app” means the app can access your location only when it’s actively open and you’re using it. This is generally recommended for most apps.
- “Always allow” means the app can access your location even when it’s closed or running in the background. This is rarely needed for most apps and can significantly drain your battery and compromise privacy. Only grant this for essential services like navigation apps.
Q6: What is “Tracking” permission on iOS? A6: The “Tracking” permission (found under Settings > Privacy & Security > Tracking) controls whether apps can track your activity across other companies’ apps and websites for advertising purposes. It’s recommended to disable this for most apps to enhance your privacy and limit targeted ads.
Common Problems and Solutions about Managing App Permissions
Even with straightforward permission management, users can encounter issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Problem 1: An app isn’t working correctly, and I suspect it’s a permission issue.
- Solution: Go into your phone’s settings, find the problematic app, and review its permissions. Ensure all necessary permissions for its core functionality are granted. The app might also display a message indicating which permission it needs. If you’re unsure, try granting the permission temporarily to see if it resolves the issue, then re-evaluate.
Problem 2: My phone battery is draining unusually fast, and I suspect an app is using excessive background permissions.
- Solution (Android): Go to Settings > Battery > Battery usage (or similar, depending on your Android version). This will show you which apps are consuming the most battery. If an app you rarely use is high on the list, check its permissions. Pay special attention to “Location” (especially “Always allow”), “Background App Refresh,” and “Microphone/Camera” if the app doesn’t require constant access.
- Solution (iPhone): Go to Settings > Battery and scroll down to “Battery Usage By App.” Identify apps with high background activity. Then, go to Settings > Privacy & Security to review permissions for those apps, or go to Settings > [App Name] to toggle off “Background App Refresh” if it’s not essential. The App Privacy Report can also highlight apps frequently accessing sensitive sensors.
Problem 3: I keep getting prompts for a permission, even after denying it.
- Solution: This usually means the app’s core functionality requires that permission. You have a few options:
- Grant the permission: If you want to use the app’s feature, you’ll need to allow it.
- Find an alternative app: If you’re uncomfortable granting the permission, look for another app that offers similar functionality with fewer or less intrusive permission requirements.
- Live without the feature: Accept that the specific feature requiring the permission won’t work in that app.
Problem 4: I’m concerned about an app requesting a permission that seems completely unrelated to its function (e.g., a calculator app asking for location).
- Solution: This is a major red flag!
- Deny the permission: Immediately deny any permission that seems unnecessary or suspicious.
- Uninstall the app: Consider uninstalling the app entirely, especially if it’s not from a reputable developer or if it insists on the unrelated permission.
- Report the app: On Google Play Store, you can report apps that exhibit suspicious behavior. Apple also provides mechanisms for reporting problematic apps.
Problem 5: I changed permissions for an app, but the changes don’t seem to take effect.
- Solution:
- Force close the app: Fully close the app from your recent apps switcher (swipe up/left on iPhone, swipe up/clear on Android) and then reopen it.
- Restart your phone: Sometimes a simple device restart can refresh system processes and apply permission changes.
- Check for app updates: Ensure the app is updated to its latest version, as bugs related to permissions might have been fixed.
Problem 6: My app permission settings are greyed out or I can’t change them.
- Solution:
- Check for parental controls or MDM: If your phone is managed by a work or school account (Mobile Device Management – MDM) or has parental controls enabled, these settings might be locked. You’ll need to contact your IT administrator or the person managing the controls.
- Specific Android cases (e.g., “Screen overlay detected”): On Android, sometimes an overlay app can prevent you from tapping “allow” on certain permissions. Disable any screen overlay apps (like chat bubbles, screen filters, or some launchers) temporarily, grant the permission, and then re-enable the overlay app. You might find “Draw over other apps” in “Special app access” settings.
By addressing these common issues, you can maintain better control over your app permissions and enhance your overall smartphone security and privacy.
Additional helpful information:
One example of app permissions is if the app can or cannot monitor your location. Read more about that here – What Apps use Location Services? Here is information about how to turn on Location Services on Android.
There are many additional things you can do to manage your privacy with the Google Privacy Settings for Android.